Exercise
Nutrition for Physical Activity with Diabetes
Nutrition and proper fuel are important components of physical activity with type 1 diabetes (T1D). Different foods can help keep blood glucose levels steady and give you enough energy to be active. There isn’t one diet that is best or works for everyone, so you might need to try different foods to find what’s best for you. A registered dietitian or diabetes educator can help you develop an individualized meal plan. This page includes some ideas on foods to eat before and after physical activity to maintain glucose levels and fuel the body for movement!
This page was developed in partnership with Leah Groppo, MS, RD, BC-ADM, CDCES, a registered dietitian and diabetes educator at Stanford Healthcare.
Pre-Activity Nutrition
Eating before physical activity helps give your body energy and can help keep your blood glucose levels in range. What you should eat depends on the kind of activity you’re doing. For example, if you're going for a long hike, your food needs might be different from when you're lifting weights. How you take insulin, like using a pump or injections, will also affect what and how much you should eat. Other things like your age, gender, and fitness level can change your food choices too Riddell MC, Gallen IW, Smart CE, et al. Exercise management in type 1 diabetes: a consensus statement. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. 2017. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/landia/article/PIIS2213-8587(17)30014-1/abstract| https://www.thelancet.com/journals/landia/article/PIIS2213-8587(17)30014-1/abstract / . It might take some time to figure out what works best for you based on the type of physical activity you enjoy.
Some important things to consider:
- Check glucose levels before starting an activity. For more information on preventing lows during physical activity, click here. For more information on how to decide how many grams of carbohydrates you may need, visit The Glucose Never Lies Exercise carbohydrate calculators - the glucose never lies. The Glucose Never Lies - The Glucose Never Lies. May 7, 2021. Accessed November 7, 2024. https://theglucoseneverlies.com/exercise-carbohydrate-calculators | https://theglucoseneverlies.com/exercise-carbohydrate-calculators / .
- Hydration is very important with physical activity. Remember that some sports drinks have carbs and may require insulin[1].
- Remember that if you eat before an activity, you may still have insulin on board by the time you start that activity Scott S, Kempf P, Bally L, Stettler C. Carbohydrate Intake in the Context of Exercise in People with Type 1 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2019;11(12):3017. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/12/3017|https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/12/3017/ .
- Timing is key when it comes to pre-activity snacks. Examples to consider include.
- Slower foods, like oatmeal, may need to be eaten about 25 to 30 minutes before physical activity.
- Faster foods, like a banana, may need to be eaten about 15 minutes before physical activity.
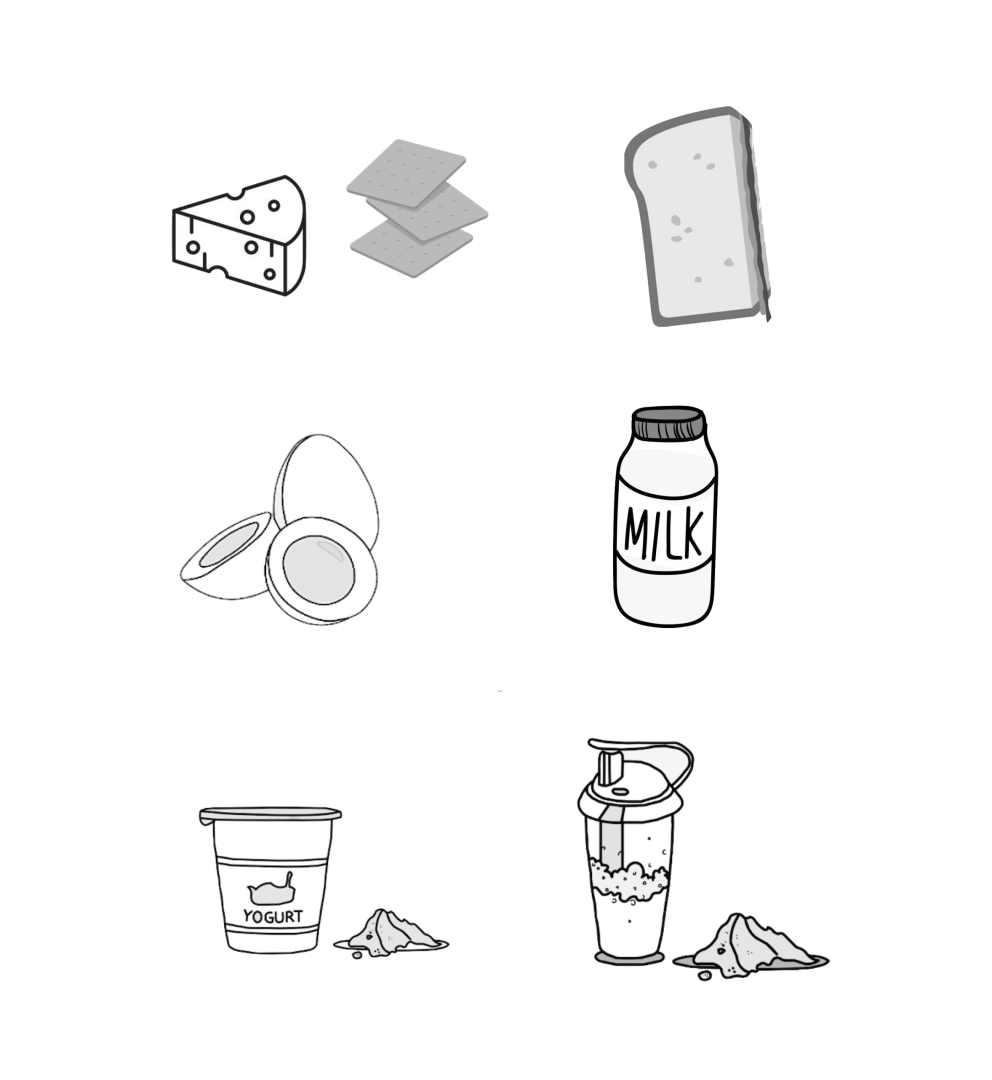
Examples of foods to consider trying before physical activity:
-
-
-
- Toast with peanut butter
- Ripe banana with a handful of almonds
- Granola bar
- Hard-boiled egg
- Energy balls made with oats
- Low-fat yogurt with protein powder
- Protein shake
-
-
Examples of foods to consider avoiding before physical activity:
-
-
-
- High-fat meals (like cheese or milkshakes) may upset the stomach and cause a delayed rise in glucose levels, so consider avoiding them if this has been your experience
- Artificial sweeteners (like aspartame or stevia) may also upset the stomach, so consider avoiding them if this has been your experience
-
-


Post-Activity Nutrition
Nutrition for recovery and to help maintain stable glucose levels after physical activity are also important. Having balanced meals with carbs and protein post-exercise can help support muscle recovery. Paying attention to the type of activity you’re doing is recommended, and how much insulin you typically take at that time of day. Again, it may take some time to figure out what works best for you based on your favorite types of activity and your body.
Some important things to consider:
- Check glucose levels when an activity is finished.
- Hydration is very important with physical activity. Remember that some sports drinks have carbohydrates and may require insulin[3].
- Eating carbs after physical activity is important to replenish energy stores in the muscles and to help prevent low glucose levels[3].
- Eating protein after physical activity has many benefits. It may help prevent delayed low blood glucose and can also help with muscle recovery Paramalingam N, Keating BL, Chetty T, et al. Protein Ingestion in Reducing the Risk of Late-Onset Post-Exercise Hypoglycemia: A Pilot Study in Adolescents and Youth with Type 1 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):543. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/3/543| https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/3/543/ .
- To promote recovery and help maintain stable blood glucose, try to eat within an hour of finishing an activity, especially if it’s a higher-intensity activity Eating tips before and after exercise. Eating Tips Before and After Exercise ADA. Accessed November 7, 2024. https://diabetes.org/health-wellness/fitness/eating-tips-before-after-exercise|https://diabetes.org/health-wellness/fitness/eating-tips-before-after-exercise/ .
Examples of snacks to consider trying after physical activity:
-
-
- Whole wheat crackers and cheese
- Half of a peanut butter and jelly sandwich
- Hard-boiled egg
- Greek yogurt with protein powder
- Smoothie with protein powder
- Milk
-